Boolean algebra is a type of algebra that is created by operating the binary system. In the year 1854, George Boole, an English mathematician, proposed this algebra. This is a variant of Aristotle’s propositional logic that uses the symbols 0 and 1, or True and False. Boolean algebra is concerned with binary variables and logic operations.
Boolean Algebra is fundamental in the development of digital electronics systems as they all use the concept of Boolean Algebra to execute commands. Apart from digital electronics this algebra also finds its application in Set Theory, Statistics, and other branches of mathematics.
In this article, we will learn about, basic Boolean operations, Boolean expressions, Truth Tables, Boolean laws, and others in detail.
Table of Content
- Boolean Algebra Operations
- Table of Boolean Algbera
- Boolean Expression and Variables
- Boolean Algebra Terminologies
- Truth Tablesin Boolean Algebra
- Boolean Algebra Rules
- Laws for Boolean Algebra
- Boolean Algebra Theorems
- Solved Examples on Boolean Algebra
Boolean Algebra Operations
There are various operations that are used in Boolean algebra but the basic operations that form the base of Boolean Algebra are.
- Negation or NOT Operation
- Conjunction or AND Operation
- Disjunction or OR Operation
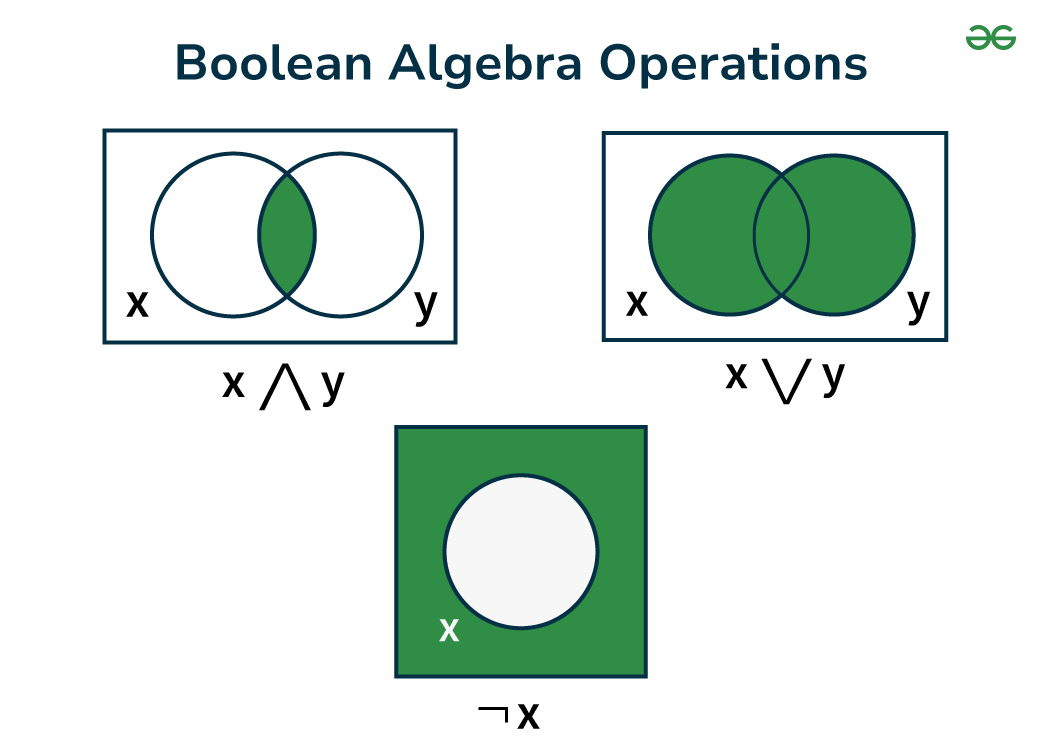
Boolean Algebra Expression
Check: Basics of Boolean Algebra in Digital Electronics
These operations have their own symbols and precedence and the table added below shows the symbol and the precedence of these operators.
Operator | Symbol | Precedence |
|---|---|---|
NOT | ‘ (or) ⇁ | First |
AND | . (or) ∧ | Second |
OR | + (or) ∨ | Third |
We can easily define these operations using two boolean variables.
Let’s take two boolean variables A and B that can have any of the two values 0 or 1, i.e. they can be either OFF or ON. Then these operations are explained as,
Negation or NOT Operation
Using the NOT operation reverse the value of the Boolean variable from 0 to 1 or vice-versa. This can be understood as:
- If A = 1, then using NOT operation we have (A)’ = 0
- If A = 0, then using the NOT operation we have (A)’ = 1
- We also represent the negation operation as ~A, i.e if A = 1, ~A = 0
Check: Properties of Boolean Algebra
Conjunction or AND Operation
Using the AND operation satisfies the condition if both the value of the individual variables are true and if any of the value is false then this operation gives the negative result. This can be understood as,
- If A = True, B = True, then A . B = True
- If A = True, B = False, Or A = false, B = True, then A . B = False
- If A = False, B = False, then A . B = False
Check: Boolean Algebraic Theorems
Disjunction (OR) Operation
Using the OR operation satisfies the condition if any value of the individual variables is true, it only gives a negative result if both the values are false. This can be understood as,
- If A = True, B = True, then A + B = True
- If A = True, B = False, Or A = false, B = True, then A + B = True
- If A = False, B = False, then A + B = False
Table of Boolean Algebra
Given Below is the Expression for the Boolean Algebra
| Operation | Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| AND Operation | ⋅ or ∧ | Returns true only if both inputs are true. |
| OR Operation | + or ∨ | Returns true if at least one input is true. |
| NOT Operation | ¬ or ∼ | Reverses the input. |
| XOR Operation | ⊕ | Returns true if exactly one input is true. |
| NAND Operation | ↓ | Returns false only if both inputs are true. |
| NOR Operation | ↑ | Returns false if at least one input is true. |
| XNOR Operation | ↔ | Returns true if both inputs are equal. |
Boolean Expression and Variables
Boolean expression is an expression that produces a Boolean value when evaluated, i.e. it produces either a true value or a false value. Whereas boolean variables are variables that store Boolean numbers.
P + Q = R is a Boolean phrase in which P, Q, and R are Boolean variables that can only store two values: 0 and 1. The 0 and 1 are the synonyms for false and True and are used in Boolean Algebra, sometimes we also use “Yes” in place of True and “No” in place of False.
Thus, we can say that statements using Boolean variables and operating on Boolean operations are Boolean Expressions. Some examples of Boolean expressions are,
- A + B = True
- A.B = True
- (A)’ = False
Check: Axioms of Boolean Algebra
Boolean Algebra Terminologies
There are various terminologies related to Boolean Algebra, which are used to explain various parameters of Boolean Algebra. That includes,
- Boolean Algebra
- Boolean Variables
- Boolean Function
- Literal
- Complement
- Truth Table
Now, we will discuss the important terminologies of Boolean algebra in the article below,
Boolean Algebra
The branch of algebra that deals with binary operations or logical operations is called Boolean Algebra. It was introduced by George Boole in the mid 19th century. It is used to analyze and manipulate logical functions in binary variables. It is extensively used in various fields such a s digital logic design, computer science and telecommunications.
Boolean Variables
Variables used in Boolean algebra that store the logical value of 0 and 1 are called the boolean variables. They are used to store either true or false values. Boolean variables are fundamental in representing logical states or propositions in Boolean expressions and functions.
Boolean Function
A function of the Boolean Algebra that is formed by the use of Boolean variables and Boolean operators is called the Boolean function. It is formed by combining Boolean variables and logical expressions such as AND, OR, and NOT. It is used to model logical relationships, conditions, or operations.
Literal
A variable or the complement of the variable in Boolean Algebra is called the Literal. Literals are the basic building blocks of the boolean expressions and functions. They represent the operands in logical operations.
Complement
The inverse of the Boolean variable is called the complement of the variable. The complement of 0 is 1 and the complement of 1 is 0. It is represented by ‘ or (¬) over the variable. Complements are used to represent logical negations in Boolean expressions and functions.
Truth Table
Table containing all the possible values of the logical variables and the combination of the variable along with the given operation is called the truth table. The number of rows in the truth table depends on the total Boolean variables used in that function. It is given by using the formula,
Number of Rows in Truth Table = 2n
where “n” is the number of Boolean variables used.
Check:
- Set Theory
- Statistics
Truth Tablesin Boolean Algebra
A truth table represents all the combinations of input values and outputs in a tabular manner. All the possibilities of the input and output are shown in it and hence the name truth table. In logic problems, truth tables are commonly used to represent various cases. T or 1 denotes ‘True’ & F or 0 denotes ‘False’ in the truth table.
Example: Draw the truth table of the conditions A + B and A.B where A and b are boolean variables.
Solution:
The required Truth Table is,
| A | B | X = A + B | Y = A.B |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | T | T | T |
| T | F | T | F |
| F | T | T | F |
| F | F | F | F |
Boolean Algebra Rules
In Boolean Algebra there are different fundamental rules for logical expression.
- Binary Representation: In Boolean Algebra the variables can have only two values either 0 or 1 where 0 represents Low and 1 represents high. These variables represents logical states of the system.
- Complement Representation: The complement of the variables is represented by (¬) or (‘) over the variable. This indicates logical negation or inversion of the variable’s value. So Complement of variable A can be represented by [Tex]\overline{A}[/Tex],if the value of A=0 then its complement is 1.
- OR Operation: The OR operation is represented by (+) between the Variables. OR operation returns true if at least one of the operands is true. For Examples let us take three variables A,B,C the OR operation can be represented as A+B+C.
- AND Operation: The AND Operation is denoted by (.) between the Variables. AND operation returns true only if all the operands are true. For Examples let us take three variables A,B,C the AND operation can be represented A.B.C or ABC.
Laws for Boolean Algebra
The basic laws of the Boolean Algebra are added in the table added below,
| Law | OR form | AND form |
|---|---|---|
| Identity Law | P + 0 = P | P.1 = P |
| Idempotent Law | P + P = P | P.P = P |
| Commutative Law | P + Q = Q + P | P.Q = Q.P |
| Associative Law | P + (Q + R) = (P + Q) + R | P.(Q.R) = (P.Q).R |
| Distributive Law | P + QR = (P + Q).(P + R) | P.(Q + R) = P.Q + P.R |
| Inversion Law | (A’)’ = A | (A’)’ = A |
| De Morgan’s Law | (P + Q)’ = (P)’.(Q)’ | (P.Q)’ = (P)’ + (Q)’ |
Let’s learn about these laws in detail.
Identity Law
In the Boolean Algebra, we have identity elements for both AND(.) and OR(+) operations. The identity law state that in boolean algebra we have such variables that on operating with AND and OR operation we get the same result, i.e.
- A + 0 = A
- A.1 = A
Commutative Law
Binary variables in Boolean Algebra follow the commutative law. This law states that operating boolean variables A and B is similar to operating boolean variables B and A. That is,
- A. B = B. A
- A + B = B + A
Associative Law
Associative law state that the order of performing Boolean operator is illogical as their result is always the same. This can be understood as,
- ( A . B ) . C = A . ( B . C )
- ( A + B ) + C = A + ( B + C)
Distributive Law
Boolean Variables also follow the distributive law and the expression for Distributive law is given as:
- A . ( B + C) = (A . B) + (A . C)
Inversion Law
Inversion law is the unique law of Boolean algebra this law states that, the complement of the complement of any number is the number itself.
- (A’)’ = A
Apart from these other laws are mentioned below:
AND Law
AND law of the Boolean algebra uses AND operator and the AND law is,
- A . 0 = 0
- A . 1 = A
- A . A = A
OR Law
OR law of the Boolean algebra uses OR operator and the OR law is,
- A + 0 = A
- A + 1 = 1
- A + A = A
De Morgan’s Laws are also called De morgan’s Theorem. They are the most important laws in Boolean Algebra and these are added below under the heading Boolean Algebra Theorem
Boolean Algebra Theorems
There are two basic theorems of great importance in Boolean Algebra, which are De Morgan’s First Laws, and De Morgan’s Second Laws. These are also called De Morgan’s Theorems. Now let’s learn about both in detail.
De Morgan’s First laws
De Morgan’s Law states that the complement of the product (AND) of two Boolean variables (or expressions) is equal to the sum (OR) of the complement of each Boolean variable (or expression).
(P.Q)’ = (P)’ + (Q)’
The truth table for the same is given below:
| P | Q | (P)’ | (Q)’ | (P.Q)’ | (P)’ + (Q)’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | T | F | F | F | F |
| T | F | F | T | T | T |
| F | T | T | F | T | T |
| F | F | T | T | T | T |
We can clearly see that truth values for (P.Q)’ are equal to truth values for (P)’ + (Q)’, corresponding to the same input. Thus, De Morgan’s First Law is true.
De Morgan’s Second laws
Statement: The Complement of the sum (OR) of two Boolean variables (or expressions) is equal to the product(AND) of the complement of each Boolean variable (or expression).
(P + Q)’ = (P)’.(Q)’
Proof:
The truth table for the same is given below:
| P | Q | (P)’ | (Q)’ | (P + Q)’ | (P)’.(Q)’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | T | F | F | F | F |
| T | F | F | T | F | F |
| F | T | T | F | F | F |
| F | F | T | T | T | T |
We can clearly see that truth values for (P + Q)’ are equal to truth values for (P)’.(Q)’, corresponding to the same input. Thus, De Morgan’s Second Law is true.
Read More,
- Properties of Boolean Algebra
- Principle of Mathematical Induction
- Logic Gates
Solved Examples on Boolean Algebra
Draw Truth Table for P + P.Q = P
Solution:
The truth table for P + P.Q = P
P Q P.Q P + P.Q T T T T T F F T F T F F F F F F In the truth table, we can see that the truth values for P + P.Q is exactly the same as P.
Draw Truth Table for P.Q + P + Q
Solution:
The truth table for P.Q + P + Q
P Q P.Q P.Q + P + Q T T T T T F F T F T F T F F F F
Solve [Tex]\textbf{\(\overline{A} + B \cdot C\)}[/Tex]
Solution:
Using De Morgan’s Law
[Tex]\overline{A}+B.C=\overline{A}.(B+C)[/Tex]
Using Distributive Law
[Tex]\overline{A}.(B+C)=\overline{A}.B+\overline{A}.C[/Tex]
So, the simplified expression for the given equation [Tex]\overline{A}.(B+C)=\overline{A}.B+\overline{A}.C[/Tex]
Conclusion
Boolean Algebra serves as a foundational framework for representing and manipulating logical expressions using binary variables and logical operators. It plays a crucial role in various fields such as digital logic design, computer programming, and circuit analysis. By providing a systematic way to describe and analyze logical relationships, Boolean Algebra enables the development of complex systems and algorithms. Its principles and operations, including AND, OR, NOT, XOR, NAND, NOR, and XNOR, form the building blocks for designing logic circuits, writing efficient code, and solving logical problems.
Boolean Algebra- FAQs
What is Boolean Algebra?
Boolean Algebra also called Logical Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with Boolean Variables such as, 0 and 1.
What are Main Boolean Operators?
There are three main Boolean Operators that are,
- AND (Conjunction)
- OR (Disjunction)
- NOT (Negation)
How to minimize Boolean Function?
There are several methods for minimizing Boolean functions, including:
- Algebraic Simplification:
- Karnaugh Maps (K-Maps):
- Quine-McCluskey Algorithm:
- Tabulation Method:
- Don’t-Care Conditions:
What are Applications of Boolean Algebra?
Boolean Algebra has various applications. It is used to simplify logical circuits that are the backbone of modern technology.
What does “0” Represent in Boolean Algebra?
The “0” in Boolean Algebra represent a False condition or it represent the Switch Off condition.
What does “1” Represent in Boolean Algebra?
The “1” in Boolean Algebra represent a True condition or it represent the Switch On condition.
What are Boolean Algebra laws?
Boolean Algebra laws are rules for manipulating logical expressions with binary variables, ensuring consistency and simplification in operations like addition, multiplication, and complementation, crucial in fields like digital electronics and computer science.
What are the 5 laws of Boolean algebra?
Boolean algebra is governed by five primary laws, which serve as the foundation for manipulating logical expressions:
1. Identity Law for AND
2. Identity Law for OR
3. Complement Law for AND
4. Complement Law for OR
5. Idempotent Law
What are the 3 laws in Boolean logic?
The three fundamental laws in Boolean logic are
- The Identity Law (adding zero or multiplying by one keeps the variable unchanged)
- The Domination Law (adding a variable to its complement results in 1 and multiplying it by its complement results in 0)
- The Commutative Law (the order of variables can be switched in addition or multiplication without changing the result).
What is De Morgan’s theorem?
De Morgan’s theorem states that the complement of a logical AND operation is equivalent to the OR operation of the complements of the individual terms, and vice versa. It’s a fundamental principle in Boolean Algebra used for simplifying logical expressions and optimizing logical circuits.
sameekshakhandelwal1712
Improve
Previous Article
What is a plane in geometry?
Next Article
Properties of Boolean Algebra